The innovation in IoT technology is an energy management unit that increases the power efficiency of electrostatic generators for sustainable solutions.
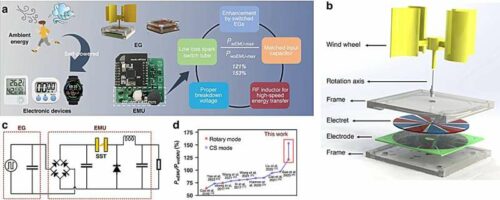
Electrostatic generators show promise in powering low-power devices in Internet of Things (IoT) networks by harnessing energy from environmental sources like wind and human motion. However, their effectiveness could be improved by an impedance mismatch when connected to electronic devices, resulting in low energy utilisation efficiency.
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed an advanced energy management unit (EMU) with exceptional performance, markedly enhancing the effectiveness of electrostatic generators tailored for Internet of Things (IoT) purposes. This innovation tackles the obstacle of high impedance mismatch encountered between electrostatic generators and electronic devices, thus paving the way for novel opportunities in ambient energy harvesting.
A recent study in Microsystems & Nanoengineering introduces a highly effective EMU tailored to substantially enhance the power efficiency of electrostatic generators utilised in IoT devices. This advancement addresses the enduring challenge of impedance mismatch, advancing the feasibility of environmental energy harvesting within the IoT realm.
The research team has notably amplified the power efficiency of electrostatic generators by implementing an innovative EMU integrated with a spark-switch tube and buck converter. This breakthrough has yielded an unprecedented direct current output of 79.2 mW m-2 rps-1 in rotary electret generators, representing a significant efficiency leap. Additionally, the EMU has bolstered the performance of contact-separated triboelectric nanogenerators by 50%, underscoring its adaptability across various energy-harvesting technologies.
This progress originates from precisely optimising key components like the spark-switch tube and a buck converter, elevating direct current power generation to unprecedented levels. This advancement surpasses current energy efficiency standards and highlights the EMU’s compatibility with diverse generator designs.
This innovation significantly improves the efficiency and reliability of self-powered IoT devices and encourages their widespread use in sustainable and remote environments. It signals the dawn of a new era of energy independence in the IoT field, representing a significant leap forward in using environmental energy harvesting for IoT applications.
Reference: Zibo Wu et al, Electrostatic generator enhancements for powering IoT nodes via efficient energy management, Microsystems & Nanoengineering (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41378-024-00660-1
The post Advanced Energy Harvesting For loT Devices appeared first on Electronics For You.
View more at https://www.electronicsforu.com/news/advanced-energy-harvesting-for-lot-devices.
Credit- EFY. Distributed by Department of EEE, ADBU: https://tinyurl.com/eee-adbu
Curated by Jesif Ahmed