The audio amplifier reference design is efficient for rapid prototyping on microcontroller platforms, enhancing audio performance.

Class-D audio amplifiers are highly valued for their efficiency, often exceeding 90%, which makes them ideal for battery-operated devices and applications where heat dissipation is a concern. Unlike traditional amplifiers that waste a significant portion of their energy as heat, Class-D amplifiers convert most of their power input into audio output, reducing energy costs and improving sustainability. Their compact size and lower heat generation allow for smaller, more portable designs. Moreover, the high efficiency of Class-D amplifiers doesn’t compromise sound quality, making them suitable for both consumer electronics and professional audio systems. The 1kW Class-D Audio Amplifier reference design from NXP Semiconductors is a model for constructing an audio amplifier with a push-pull power converter. It operates on the Kinetis KV1x Tower series platform. This design utilizes the internal FlexTimer module to modulate the input analogue audio in a Class-D format and generate PWM signals to control the switching push-pull power supply.
The 1kW Class-D Audio Amplifier boasts several features that streamline its design and enhance its performance. It enables rapid prototyping using either the Tower System module or the Freedom System platform, essential for capturing analog audio input, generating Class-D audio output, and controlling the push-pull power supply. The amplifier comes with embedded source code, allowing for the quick and cost-effective construction of a Class-D audio amplifier. Additionally, the FlexTimer manages the gate drivers for the power MOSFETs, incorporating several protections such as dead-time insertion, fault control, initialization, and polarity control. This efficient design minimizes CPU load, freeing up the processor for further application enhancements.
The FlexTimer feature in the system controls the gate drivers for power MOSFETs, adding several layers of protection, including dead-time insertion, fault control, initialization, and polarity control. This setup ensures operational safety and reliability while minimizing the CPU load. As a result, more processor resources remain available for enhancing and expanding applications.
The tools and software required for operation include the TWR-KV10Z32 module and the Kinetis Design Studio version 3.0.0 or higher. These components are essential for the system’s setup and functionality.
NXP has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, a design file, etc. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.
The post Class D Audio Amplifier Reference Design appeared first on Electronics For You.
View more at https://www.electronicsforu.com/electronics-projects/class-d-audio-amplifier-reference-design.
Credit- EFY. Distributed by Department of EEE, ADBU: https://tinyurl.com/eee-adbu
Curated by Jesif Ahmed













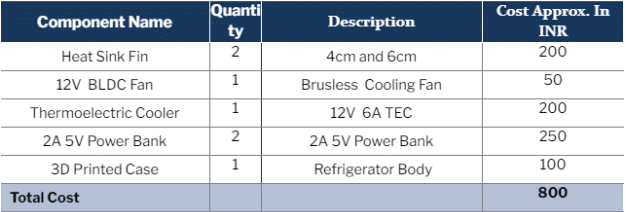
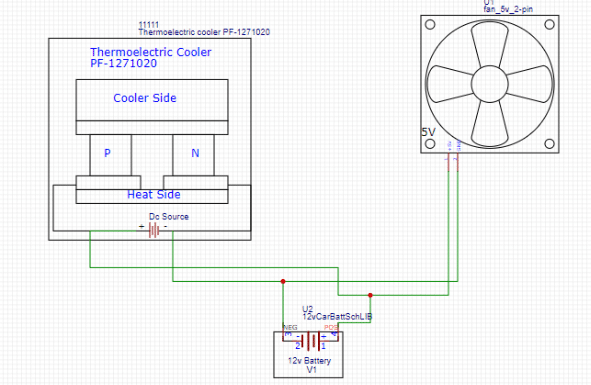
 A Mini Fridge that can work with any power bank and without using harmful CFC gases.
A Mini Fridge that can work with any power bank and without using harmful CFC gases.