Voltage sources in a circuit may have fluctuations resulting in not providing fixed voltage outputs. A voltage regulator IC maintains the output voltage at a constant value. 7805 Voltage Regulator, a member of the 78xx series of fixed linear voltage regulators used to maintain such fluctuations, is a popular voltage regulator integrated circuit (IC).
The xx in 78xx indicates the output voltage it provides. 7805 IC provides +5 volts regulated power supply with provisions to add a heat sink.
7805 Voltage Regulator IC Specifications
- Minimum Input voltage is 7V
- Maximum Input Voltage is 35V
- Current rating Ic = 1A
- Maximum Output Voltage VMax=5.2V
- Minimum Output Voltage VMin=4.8V
LM7805 Voltage Regulator Pinout
Below you can see the 7805 Voltage Regulator Pin Diagram.
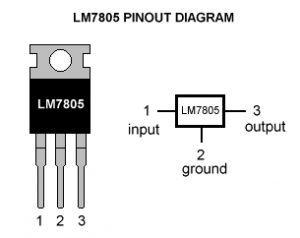
| Pin No. | Pin | Function | Description |
| 1 | INPUT | Input voltage (7V-35V) | In this pin of the IC positive unregulated voltage is given in the regulation. |
| 2 | GROUND | Ground (0V) | In this pin where the ground is given. This pin is neutral for equally the input and output. |
| 3 | OUTPUT | Regulated output; 5V (4.8V-5.2V) | The output of the regulated 5V is taken out at this pin of the IC regulator. |
As you may have noticed, there is a significant difference between the input voltage & the output voltage of the voltage regulator. This difference between the input and output voltage is released as heat. The greater the difference between the input and output voltage, more the heat is generated.
If the regulator does not have a heat sink to dissipate this heat, it can get destroyed and malfunction. Hence, it is advisable to limit the voltage to a maximum of 2-3 volts above the output voltage.
So, we now have 2 options. Either design your circuit so that the input voltage going into the regulator is limited to 2-3 volts above the output regulated voltage or place an appropriate heatsink, that can efficiently dissipate heat.
7805 IC Heating Problem
7805 voltage regulator is not very efficient and has drop-out voltage problems. A lot of energy is wasted in the form of heat. If you are going to be using a heatsink, better calculate the heatsink size properly. The below formula should help in determining the appropriate heatsink size for such applications.
Heat generated = (input voltage – 5) x output current
If we have a system with an input of 15 volts and the output current required is .5 amperes,
Then we have: (15 – 5) x 0.5 = 10×0.5 = 5W;
5W energy is being wasted as heat, hence an appropriate heatsink is required to disperse this heat. On the other hand, the energy actually being used is: (5 x 0.5Amp) = 2.5W.
So twice the energy, that is actually utilized is wasted. On the other hand, if 9V is given as input at the same amount of load: (9-5) x 0.5 = 2W
2W energy will be wasted as heat.
What should we do then?
Remember… higher the input voltage, the less efficient your IC7805 will be.
An estimated efficient input voltage would be about 7.5V.
Why do we use Capacitors with 7805?
If your voltage regulator is situated more than 25cm (10 inches) from the power supply, capacitors are needed to filter residual AC noise. Voltage regulators work efficiently on a clean DC signal being fed. The bypass capacitors help reduce AC ripple.
Essentially, they short AC noise from the voltage signal and allow only DC voltage into the regulator. The two capacitors are not necessarily required and can be omitted if you are not concerned about line noise.
However, for a mobile phone charger or logic assessment, you require a nice clean DC line. Capacitors will be beneficial in this case as they are good at maximizing voltage regulation. The values of capacitors can also be changed slightly.
You can check Why Are Filter Capacitors Used in Some Battery Charger Circuits?
Let’s take a look at what makes the IC tick.
Voltage Regulator 7805 IC Circuit
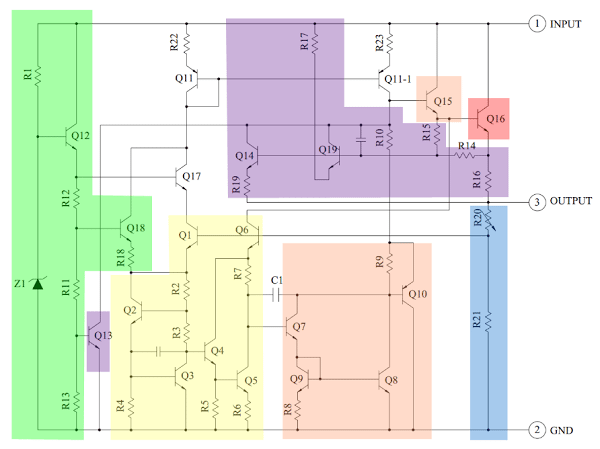
The heart of the 7805 IC is a transistor (Q16) that controls the current between the input and output and thus controls the output voltage. The bandgap reference (yellow) keeps the voltage stable.
It takes the scaled output voltage as input (Q1 and Q6) and provides an error signal (to Q7) for indication if the voltage is too high or low.
The key task of the bandgap is to provide a stable and accurate reference, even as the chip’s temperature changes.
The error signal from the bandgap reference is amplified by the error amplifier (orange). This amplified signal controls the output transistor through Q15. This closes the negative feedback loop controlling the output voltage.
The startup circuit (green) provides initial current to the bandgap circuit, so it doesn’t get stuck in an “off” state. The circuit in purple provides protection against overheating (Q13), excessive input voltage (Q19), and excessive output current (Q14).
These circuits reduce the output current or shut down the regulator, protecting it from damage in case of a fault. The voltage divider (blue) scales down the voltage on the output pin for use by the bandgap reference.
Scaling the Output
The 7805’s scaled output provides the input voltage (Vin) to the bandgap reference and the bandgap provides an error signal as the output. The 7805’s bandgap circuit removes the feedback loop that exists inside a traditional bandgap reference. Instead, the entire chip becomes the feedback loop.
If the output voltage is correct (5V), then the voltage divider provides 3.75V at Vin. Any change in output voltage propagates through Q6 and R7, causing the voltage at the base of Q7 to rise or fall accordingly.
This change is amplified by Q7 and Q8, generating the error output. The error output, in turn, decreases or increases the current through the output transistor. The negative feedback loop adjusts the output voltage until it is correct.
IC 7805 Voltage Regulator Applications
7805 IC is used in a wide range of circuits. The major ones are:
- Fixed-Output Regulator
- Positive voltage Regulator in Negative voltage Configuration
- Adjustable Output Regulator
- Current Regulator
- Adjustable DC Voltage Regulator
- Regulated Dual-Supply
- Output Polarity-Reversal-Protection Circuit
- Reverse bias projection Circuit
7805 Voltage regulator also finds usage in building circuits for inductance meters, phone chargers, portable CD player, infrared remote-control extension, and UPS power supply circuits. Also, we designed a Stopwatch Circuit using IC7805.
The slideshow below also highlights some points with voltage regulators.
Complete technical detailed information about the 7805-voltage regulator IC can be found in the 7805 IC datasheet.
What does a 7805 voltage regulator do?
A 7805 voltage regulator is an integrated circuit designed to maintain a constant output voltage despite changes in input voltage and load. Specifically, the 7805 is a positive voltage regulator that ensures a stable +5V output, making it a popular choice for powering various electronic components and circuits.
How much voltage can 7805 handle?
The 7805 voltage regulator is typically used to provide a fixed +5V output. To ensure proper operation, the input voltage should be higher than the desired output voltage plus a small overhead voltage for the regulator to function correctly. Generally, the input voltage can range from around 7V to 35V, allowing the 7805 to handle a wide range of input voltages while maintaining a steady +5V output.
What temperature should a 7805 voltage regulator be?
The operating temperature of a 7805 voltage regulator is typically specified by its manufacturer. Standard operating temperature ranges are often from 0°C to 125°C. However, variations exist, and some models might have extended temperature ranges to accommodate specific applications.
What is the difference between LM7805 and 7805?
The terms “LM7805” and “7805” both refer to the same type of voltage regulator. The LM prefix indicates that the component is manufactured by National Semiconductor (now a part of Texas Instruments), and it’s often included for clarity. So, the LM7805 and 7805 both represent the same voltage regulator with a fixed +5V output.
View more at https://www.electronicsforu.com/technology-trends/learn-electronics/7805-ic-voltage-regulator.
Credit- EFY. Distributed by Department of EEE, ADBU: https://tinyurl.com/eee-adbu
Curated by Jesif Ahmed